Executive Summary
In today's interconnected digital landscape, marketing professionals face unprecedented challenges in balancing effective data-driven strategies with increasingly complex global privacy regulations. This whitepaper examines the current state of data security and compliance in digital marketing, with a particular focus on how businesses operating across multiple international markets can navigate diverse regulatory frameworks while maintaining marketing effectiveness.
Key findings include:
- The global regulatory landscape continues to fragment, with significant variations between GDPR (EU), CCPA/CPRA (California), PDPA (Singapore), and other regional frameworks
- Organizations implementing robust compliance programs report 23% fewer data breaches and 35% faster resolution times when incidents occur
- Privacy-centric marketing approaches are showing promising results, with 67% of consumers more likely to engage with brands that demonstrate strong data protection practices
- Cross-border data transfers remain a significant challenge, particularly for businesses operating between Asia, Europe, and North America
- AI and automation technologies present both new compliance risks and opportunities for more secure, efficient marketing operations
This document provides marketing leaders and compliance professionals with practical frameworks, implementation strategies, and real-world case studies to develop effective, compliant marketing programs across diverse global markets.
Introduction: The Evolving Data Security Landscape
The digital marketing ecosystem has undergone a profound transformation in recent years. As organizations increasingly rely on customer data to drive personalized experiences and targeted campaigns, they face mounting pressure from both regulatory bodies and consumers to handle this information responsibly and transparently.
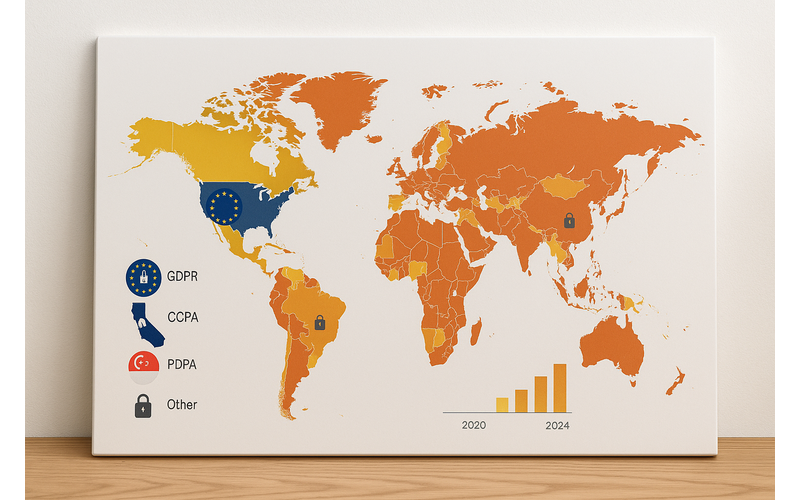 Figure 1: The evolving global data privacy landscape, 2020-2024
Figure 1: The evolving global data privacy landscape, 2020-2024
For marketing professionals operating across international boundaries, this challenge is particularly acute. Different regions have developed distinct approaches to data protection, creating a complex patchwork of requirements that can vary dramatically from one market to another. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) established a comprehensive framework that has influenced legislation worldwide, but significant variations exist in how different countries approach issues like consent, data localization, and breach notification.
Meanwhile, high-profile data breaches continue to make headlines, eroding consumer trust and demonstrating the very real business consequences of security failures. In 2023 alone, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million globally, with marketing databases among the most frequently targeted systems.
"The most successful organizations no longer view data privacy as merely a compliance exercise, but as a strategic business advantage that builds customer trust and differentiates their brand in the marketplace."
— Maria Chen, Chief Privacy Officer, Aries Star Marketing OPC
This whitepaper explores how forward-thinking marketing organizations are navigating this complex landscape, implementing robust security and compliance frameworks that protect sensitive information while enabling effective, data-driven marketing strategies across global markets.
Key Regulatory Frameworks Affecting Global Marketing
Marketing professionals must navigate an increasingly complex web of data protection regulations that vary by region. Understanding the key requirements of major frameworks is essential for developing compliant global marketing strategies.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - European Union
Implemented in May 2018, the GDPR remains the most comprehensive data protection framework globally. Key provisions affecting marketing include:
- Explicit Consent: Marketing activities typically require clear, affirmative consent that is "freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous"
- Right to Be Forgotten: Individuals can request deletion of their personal data
- Data Portability: Consumers can request their data in a machine-readable format
- Privacy by Design: Data protection must be built into systems from the outset
- Significant Penalties: Fines of up to 4% of global annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) & California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)
California's framework affects many global companies targeting U.S. consumers. Key provisions include:
- Opt-Out Model: Consumers must be able to opt out of data sales and sharing
- Right to Know: Consumers can request disclosure of collected personal information
- Non-Discrimination: Businesses cannot discriminate against consumers exercising their rights
- Expanded Definition of "Sale": Includes sharing data for advertising purposes
Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) - Singapore
A key framework for businesses operating in Southeast Asia:
- Consent Obligation: Organizations must obtain consent before collecting, using, or disclosing personal data
- Purpose Limitation: Data can only be used for the purposes for which it was collected
- Data Breach Notification: Mandatory reporting of significant breaches
- Data Transfer Limitations: Restrictions on cross-border data transfers
| Regulation |
Key Marketing Implications |
Territorial Scope |
Penalties |
| GDPR (EU) |
Explicit consent required; strict limitations on profiling |
Applies to all EU data subjects regardless of company location |
Up to €20M or 4% of global revenue |
| CCPA/CPRA (California) |
Opt-out rights for data sales and sharing; transparency requirements |
Applies to businesses meeting revenue or data processing thresholds |
$2,500-$7,500 per violation |
| PDPA (Singapore) |
Consent-based framework; purpose limitation |
Applies to all organizations collecting data in Singapore |
Up to SGD 1 million |
| LGPD (Brazil) |
Similar to GDPR; legal bases for processing |
Applies to data processing in Brazil or targeting Brazilian individuals |
Up to 2% of revenue in Brazil (capped at R$50M per violation) |
| PIPL (China) |
Strict data localization; separate consent for cross-border transfers |
Applies to processing of Chinese residents' data |
Up to CNY 50 million or 5% of annual revenue |
Key Challenge: Regulatory Fragmentation
The proliferation of data protection laws creates significant compliance challenges for global marketing teams. While many frameworks share common principles, important differences in implementation, enforcement, and specific requirements necessitate market-specific approaches rather than one-size-fits-all compliance strategies.
Security Risks in Digital Marketing
Marketing departments often manage vast quantities of sensitive customer data, making them prime targets for security threats. Understanding these risks is essential for implementing appropriate safeguards.
Common Security Vulnerabilities in Marketing Operations
- Third-Party Integrations: Marketing technology stacks often include numerous third-party tools and platforms, each representing a potential security vulnerability. According to recent research, 63% of data breaches involve third-party access.
- Data Collection Points: Lead generation forms, landing pages, and other customer touchpoints can be vulnerable to injection attacks and other exploits if not properly secured.
- Customer Databases: Marketing databases containing personal information are high-value targets for attackers, particularly when they contain financial or identity information.
- Email Marketing Systems: Compromised email marketing platforms can be used to distribute malware or phishing attempts that appear to come from trusted brands.
- Analytics and Tracking: Website analytics and tracking tools often process large volumes of user data and can create security risks if not properly implemented.
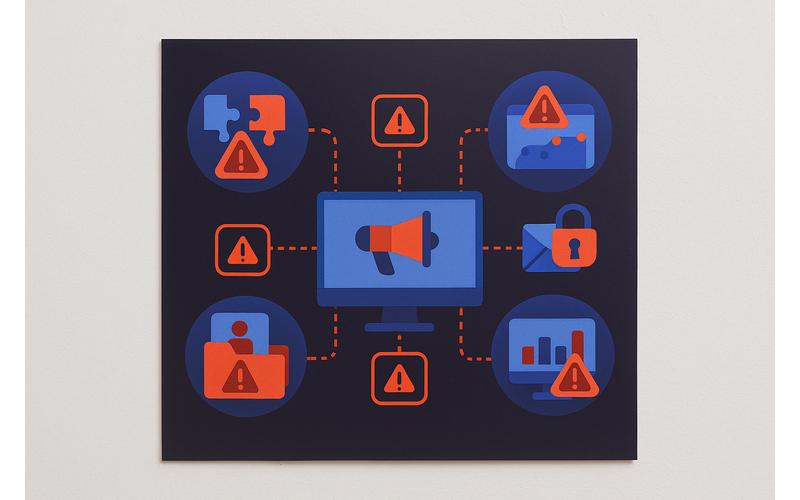 Figure 2: Common security threats affecting marketing operations
Figure 2: Common security threats affecting marketing operations
Emerging Threat Vectors
The threat landscape continues to evolve, with several emerging risks of particular concern to marketing teams:
- AI-Generated Phishing: Sophisticated phishing attempts using AI to mimic brand communications with unprecedented accuracy.
- API Vulnerabilities: As marketing systems become more interconnected through APIs, these connection points represent growing attack surfaces.
- Synthetic Identity Fraud: Fraudsters combining real and fabricated information to create convincing fake identities that can bypass verification systems.
- Cross-Device Tracking Exploits: Vulnerabilities in technologies that track users across multiple devices.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Compromises of marketing vendors or service providers that can affect multiple clients simultaneously.
Case Example: The MarTech Supply Chain Attack
In late 2023, a major marketing automation platform was compromised through a sophisticated supply chain attack. The attackers injected malicious code into a software update, which was then distributed to thousands of marketing departments worldwide. The breach affected over 300 companies across 27 countries, exposing customer data and allowing attackers to modify tracking scripts to harvest additional information. Total estimated damages exceeded $150 million.
Building a Global Marketing Compliance Framework
Developing an effective compliance framework requires a structured approach that addresses both regulatory requirements and security best practices while enabling marketing teams to operate efficiently across diverse markets.
Core Components of an Effective Compliance Program
- Data Mapping and Classification
Begin by thoroughly documenting what personal data your marketing operations collect, where it's stored, how it flows through your systems, and which third parties have access. Classify data based on sensitivity and applicable regulatory requirements.
- Risk Assessment
Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in your marketing technology stack, processes, and third-party relationships. Prioritize risks based on likelihood and potential impact.
- Policy Development
Develop clear, comprehensive policies governing data collection, usage, retention, and security in marketing activities. These should address both global standards and market-specific requirements.
- Privacy Notices and Consent Management
Implement transparent privacy notices and robust consent mechanisms that meet the highest applicable standards while being adaptable to different regional requirements.
- Vendor Management
Establish a rigorous process for vetting, contracting with, and monitoring marketing technology vendors and service providers, with particular attention to their data security and compliance capabilities.
- Training and Awareness
Provide regular training for marketing team members on data protection principles, security best practices, and compliance requirements relevant to their roles.
- Incident Response Planning
Develop and regularly test incident response procedures specific to marketing-related data breaches or compliance failures.
- Compliance Monitoring and Auditing
Implement ongoing monitoring of marketing activities and periodic audits to verify compliance with policies and regulatory requirements.
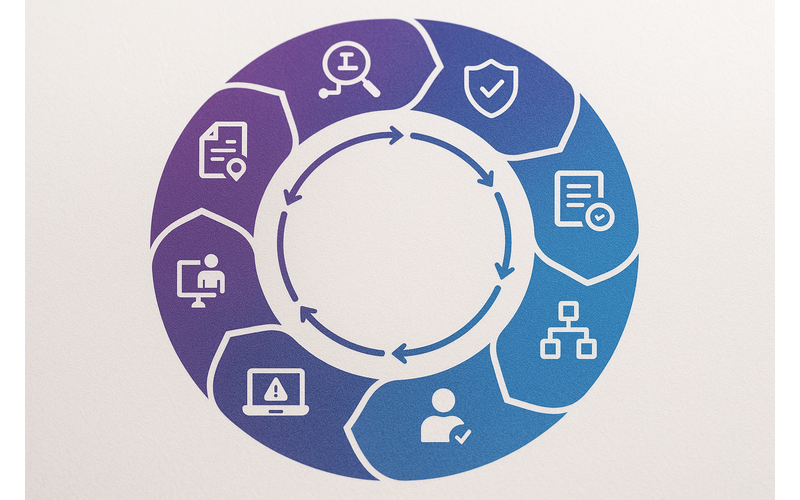 Figure 3: Integrated approach to global marketing compliance
Figure 3: Integrated approach to global marketing compliance
Region-Specific Implementation Strategies
| Region |
Key Considerations |
Implementation Priorities |
| European Union |
Strict consent requirements; comprehensive data subject rights |
Granular consent mechanisms; robust data subject request handling; legitimate interest assessments |
| North America |
Varied state-level requirements; opt-out focused |
State-specific privacy notices; "Do Not Sell/Share" mechanisms; data inventory mapping |
| Asia-Pacific |
Data localization requirements; cross-border transfer restrictions |
Local data storage solutions; transfer impact assessments; consent management |
| Middle East |
Emerging regulatory frameworks; sector-specific requirements |
Flexible compliance architecture; enhanced security measures; cultural sensitivity |
Case Studies: Compliance Success Stories
The following case studies illustrate how organizations have successfully implemented robust compliance frameworks while maintaining effective marketing operations across multiple regions.
Case Study 1: Global Retail Brand Harmonizes Compliance Across 30+ Markets

Challenge: A multinational retail brand operating in over 30 countries faced significant challenges maintaining consistent data protection standards while addressing diverse local requirements. Their decentralized marketing operations had resulted in fragmented approaches to compliance, creating both legal risks and operational inefficiencies.
Solution: Working with Aries Star Marketing OPC, the company implemented a "global baseline, local adaptation" framework. This included:
- Development of core global data protection standards based on the most stringent applicable requirements
- Creation of a centralized consent management platform with region-specific configurations
- Implementation of a global marketing data inventory with real-time visibility
- Establishment of a cross-functional privacy governance committee with regional representatives
Results: 42% reduction in compliance management costs, elimination of 3 regulatory investigations, and 28% improvement in consent rates through enhanced transparency.
Case Study 2: Financial Services Provider Secures Marketing Ecosystem

Challenge: A leading financial services provider with operations in Asia and the Middle East needed to enhance security across its marketing technology ecosystem while maintaining the ability to deliver personalized customer experiences. The company was particularly concerned about third-party vendor risks and cross-border data transfers.
Solution: The company partnered with Aries Star to implement a comprehensive security enhancement program:
- Conducted security assessments of all marketing technology vendors and implemented a tiered risk management approach
- Deployed data minimization techniques to reduce sensitive data exposure
- Implemented API security gateways to protect data flows between marketing systems
- Established regional data processing hubs to address data localization requirements
- Developed anonymized analytics capabilities to reduce reliance on personal data
Results: Zero security incidents over 18 months, 64% reduction in sensitive data exposure, and successful expansion into three new markets with complex regulatory requirements.
Practical Implementation Guide
Implementing a robust data security and compliance program requires a structured approach. The following roadmap provides practical guidance for marketing leaders seeking to enhance their compliance posture while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (1-2 Months)
- Conduct a comprehensive data mapping exercise to identify all personal data in marketing systems
- Perform a gap analysis against applicable regulatory requirements
- Assess current security controls and identify vulnerabilities
- Develop a prioritized remediation roadmap
- Establish a cross-functional implementation team with clear responsibilities
Phase 2: Foundation Building (2-3 Months)
- Develop or update privacy policies and notices
- Implement consent management infrastructure
- Establish data subject/consumer rights fulfillment processes
- Enhance security controls for highest-risk systems
- Develop incident response procedures
- Create initial training materials
Phase 3: Implementation and Integration (3-4 Months)
- Deploy technical solutions across marketing technology stack
- Integrate privacy controls into marketing workflows
- Implement vendor management program
- Conduct staff training
- Develop compliance documentation
- Establish monitoring mechanisms
Phase 4: Optimization and Maturity (Ongoing)
- Conduct regular compliance audits
- Refine processes based on operational feedback
- Monitor regulatory developments and update program accordingly
- Implement advanced security measures
- Develop metrics to measure program effectiveness
- Establish continuous improvement cycle
Key Success Factors
Organizations that successfully implement effective compliance programs typically share several common characteristics:
- Executive Sponsorship: Clear support from senior leadership
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Active involvement from marketing, IT, legal, and security teams
- Balanced Approach: Focus on both compliance requirements and business objectives
- Appropriate Resources: Dedicated budget and personnel
- Continuous Improvement: Regular assessment and refinement of the program
Future Trends and Emerging Considerations
The data protection landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Marketing leaders should monitor the following trends that are likely to shape compliance requirements in the coming years:
Regulatory Evolution
- Global Convergence: While regional variations will persist, we're seeing increasing alignment around core principles like transparency, purpose limitation, and individual rights
- Algorithmic Accountability: Growing regulatory focus on automated decision-making, profiling, and AI-driven marketing
- Children's Privacy: Expanded protections for minors' data with significant implications for brands targeting younger demographics
- Enforcement Escalation: More aggressive enforcement actions with higher penalties, particularly for repeat offenders
Technological Developments
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Growing adoption of advanced techniques like federated learning, differential privacy, and homomorphic encryption that enable data analysis while preserving privacy
- Cookieless Tracking Alternatives: New approaches to user identification and measurement as third-party cookies are phased out
- Blockchain for Consent Management: Distributed ledger technologies providing immutable records of consent
- AI-Powered Compliance: Machine learning tools that can automate aspects of compliance monitoring and risk assessment
Market Dynamics
- Privacy as a Competitive Advantage: Growing consumer preference for brands with strong privacy practices
- First-Party Data Premium: Increased value of consensually collected first-party data as privacy regulations restrict other data sources
- Vendor Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions in the privacy technology space creating more comprehensive solutions
- Global Talent Shortage: Continuing challenges in recruiting and retaining privacy and security expertise
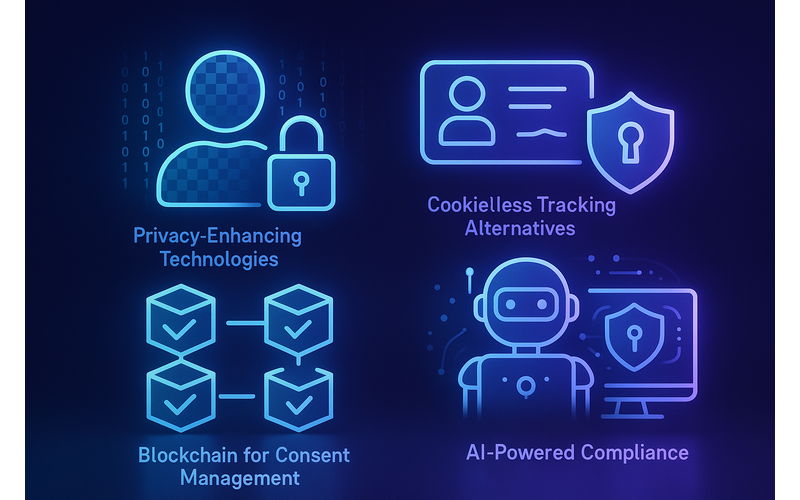 Figure 4: Emerging trends in data privacy and security
Figure 4: Emerging trends in data privacy and security
Conclusion and Recommendations
As data protection regulations continue to evolve globally, marketing organizations face both challenges and opportunities. Those that successfully navigate this complex landscape can not only mitigate compliance risks but also build stronger customer relationships based on trust and transparency.
Based on our research and experience working with global clients, we recommend the following approaches:
Strategic Recommendations
- Adopt Privacy by Design: Integrate privacy considerations into marketing processes from the earliest stages rather than treating compliance as an afterthought
- Implement a Tiered Approach: Develop a global baseline that meets the most stringent requirements, with market-specific adaptations where necessary
- Prioritize Data Minimization: Collect and retain only the data necessary for specific, documented purposes
- Invest in First-Party Data: Develop strategies to ethically collect and leverage first-party data with clear consent
- Build Cross-Functional Governance: Establish collaborative processes between marketing, legal, IT, and security teams
Tactical Recommendations
- Conduct Regular Assessments: Implement quarterly privacy impact assessments for marketing activities
- Enhance Vendor Management: Develop rigorous security and privacy requirements for marketing technology vendors
- Implement Robust Consent Management: Deploy flexible consent mechanisms that can adapt to different regulatory requirements
- Develop Incident Response Capabilities: Create and test marketing-specific data breach response procedures
- Invest in Training: Provide ongoing education for marketing teams on evolving privacy requirements
"The organizations that will thrive in the privacy-first future are those that view data protection not as a compliance burden, but as an opportunity to differentiate their brand and build deeper customer relationships based on trust."
— David Nguyen, CEO, Aries Star Marketing OPC
By implementing these recommendations, marketing leaders can navigate the complex global regulatory landscape while continuing to deliver effective, data-driven campaigns that respect consumer privacy and build lasting trust.









