Introduction to Cross-Platform Mobile Development
In today's digital landscape, having a mobile presence is no longer optional for businesses. With over 6.8 billion smartphone users worldwide split between iOS and Android, reaching your entire audience requires applications that work seamlessly across multiple platforms.
Traditional native development approaches require maintaining separate codebases for iOS and Android, effectively doubling development effort, time, and cost. Cross-platform development offers a compelling alternative: write once, deploy everywhere.
 Native vs Cross-Platform Development Approaches
Native vs Cross-Platform Development Approaches
This comprehensive guide explores the world of cross-platform mobile development, comparing leading frameworks, analyzing their strengths and limitations, and providing a strategic roadmap for choosing the right approach for your business needs.
Whether you're a business leader evaluating technology options, a product manager planning your mobile strategy, or a developer exploring cross-platform tools, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your mobile development approach.
Comparing Popular Cross-Platform Frameworks
The cross-platform development landscape offers several mature frameworks, each with distinct approaches, performance characteristics, and ecosystem advantages. Let's examine the three leading contenders:
React Native
Developed by Facebook (now Meta), React Native has become one of the most widely adopted cross-platform frameworks since its release in 2015. It uses JavaScript and React to create truly native mobile applications.
 React Native Architecture and Component Example
React Native Architecture and Component Example
Flutter
Google's Flutter has gained tremendous momentum since its stable release in 2018. Unlike other frameworks, Flutter doesn't use native components but renders everything using its own high-performance rendering engine.
 Flutter Architecture and Widget Example
Flutter Architecture and Widget Example
Xamarin
Microsoft's Xamarin allows developers to use C# and .NET to build applications for multiple platforms. It offers deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem and appeals particularly to organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies.
 Xamarin Architecture and Code Example
Xamarin Architecture and Code Example
Framework Comparison
Let's compare these frameworks across key dimensions that matter for business and technical decision-making:
| Feature |
React Native |
Flutter |
Xamarin |
| Language |
JavaScript/TypeScript |
Dart |
C#/.NET |
| UI Approach |
Native components |
Custom rendering engine |
Native components |
| Performance |
Very good |
Excellent |
Good |
| Learning Curve |
Moderate (familiar to web devs) |
Moderate |
Steep (for non-.NET devs) |
| Community Size |
Very large |
Large and growing |
Moderate |
| Corporate Backing |
Meta (Facebook) |
Google |
Microsoft |
| App Size |
Moderate |
Larger |
Larger |
| Hot Reload |
Yes |
Yes |
Limited |
| Native API Access |
Good |
Good |
Excellent |
| Ideal For |
Web developers, startups |
Complex UIs, animations |
.NET shops, enterprise |
Advantages and Limitations of Cross-Platform Development
Before committing to a cross-platform approach, it's essential to understand both the benefits and potential drawbacks compared to native development:
Advantages
- Significantly reduced development time and cost (up to 30-40%)
- Single codebase maintenance across platforms
- Faster time-to-market for both iOS and Android
- Easier team scaling with fewer platform specialists needed
- Consistent user experience across platforms
- Access to a larger talent pool (especially for JavaScript/React developers)
- Simplified updates and feature parity management
- Lower long-term maintenance costs
Limitations
- Potential performance limitations for graphics-intensive applications
- Delayed access to newest platform features and APIs
- Framework-specific limitations and workarounds
- Dependency on third-party libraries for platform-specific functionality
- Larger app size compared to optimized native apps
- Learning curve for framework-specific patterns and tools
- Potential debugging complexity for platform-specific issues
- Risk of framework abandonment or major changes
When to Choose Cross-Platform Development
Cross-platform development is particularly well-suited for:
Startups and MVPs
When speed to market and budget efficiency are critical, cross-platform development allows rapid deployment across both major platforms with minimal resources.
Content-Focused Apps
Applications that primarily display content, handle form inputs, or manage data without intensive graphics or hardware integration are ideal candidates.
Enterprise Applications
Internal business applications that need deployment across employee devices benefit from the consistency and maintenance efficiency of cross-platform approaches.
E-commerce and Service Apps
Customer-facing applications that need to reach the widest possible audience quickly while maintaining consistent branding and functionality.
When to Consider Native Development
Native development might still be preferable for:
- Graphics-intensive games requiring maximum performance
- Applications heavily relying on platform-specific features or hardware
- Apps requiring specialized device integrations not well-supported by cross-platform frameworks
- Projects where the team already has strong platform-specific expertise
Technical Considerations for Cross-Platform Development
Beyond the high-level comparison, several technical factors should influence your cross-platform development strategy:
Performance Optimization
While modern cross-platform frameworks deliver impressive performance, optimizing your application requires understanding framework-specific best practices:
- React Native: Minimize bridge crossings between JavaScript and native code, use native driver for animations, implement virtualized lists for large data sets
- Flutter: Leverage the widget tree efficiently, use const constructors, implement proper state management, avoid unnecessary rebuilds
- Xamarin: Utilize platform-specific optimizations, minimize unnecessary marshaling, implement proper memory management
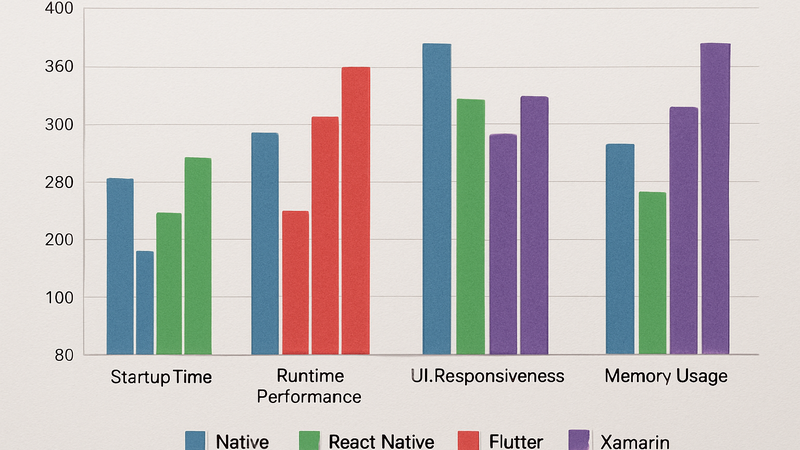 Performance Comparison Between Native and Cross-Platform Frameworks
Performance Comparison Between Native and Cross-Platform Frameworks
Native Feature Access
All major cross-platform frameworks provide mechanisms to access platform-specific APIs and features:
- React Native: Native modules system allows JavaScript to communicate with native code
- Flutter: Platform channels enable communication between Dart and native code
- Xamarin: Direct access to platform-specific APIs through bindings
For functionality not covered by the framework or existing plugins, you'll need to develop native bridges or modules. This requires some platform-specific knowledge but is well-documented in each framework.
UI/UX Considerations
Cross-platform development presents unique UI/UX challenges and opportunities:
- Platform-Specific Design: Decide whether to follow platform-specific design guidelines (Material Design for Android, Human Interface Guidelines for iOS) or create a custom, consistent design language
- Component Libraries: Leverage framework-specific UI libraries that implement platform design patterns
- Responsive Design: Implement responsive layouts that adapt to different screen sizes and orientations across device types
- Gesture Handling: Ensure gesture interactions feel natural on each platform
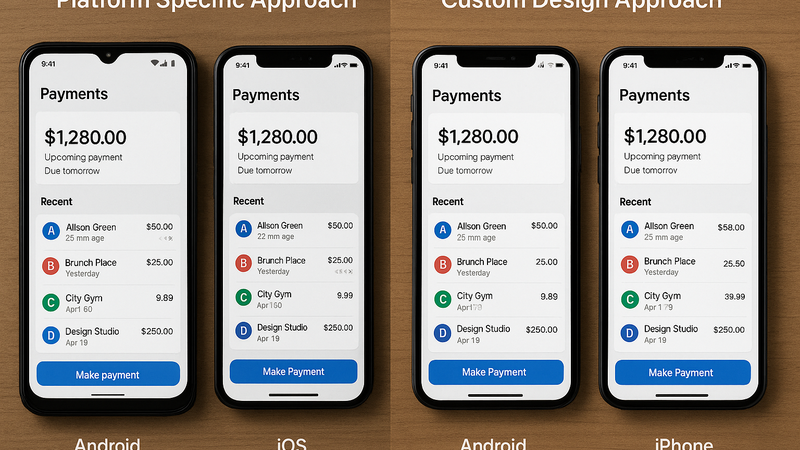 Platform-Specific vs Custom Design Approaches
Platform-Specific vs Custom Design Approaches
Testing Strategy
A comprehensive testing strategy for cross-platform applications should include:
- Unit Testing: Framework-specific testing tools (Jest for React Native, Flutter Test for Flutter, xUnit for Xamarin)
- Integration Testing: Testing component interactions within the application
- UI Testing: Automated UI tests using tools like Detox (React Native), Flutter Driver, or Xamarin.UITest
- Platform-Specific Testing: Targeted testing for platform-specific features and integrations
- Device Testing: Testing on a representative sample of physical devices or device farms
Cross-Platform Success Stories
Many organizations have successfully implemented cross-platform strategies. Here are some notable examples:
Retail Giant's Omnichannel App Transformation
A leading Southeast Asian retail chain needed to replace their aging native apps with a modern, feature-rich shopping experience across iOS and Android. By adopting Flutter, they achieved:
- 40% reduction in development time compared to their previous native approach
- Single codebase maintained by a unified team instead of separate iOS and Android teams
- Consistent brand experience and feature parity across platforms
- 30% increase in mobile conversion rates due to improved performance and UX
- Faster feature deployment cycles (2 weeks vs 4-6 weeks previously)
Financial Services App with React Native
A Middle Eastern banking institution leveraged React Native to create a comprehensive mobile banking application that needed to meet strict security and performance requirements:
- Achieved 95% code sharing between iOS and Android platforms
- Integrated seamlessly with native security modules and biometric authentication
- Reduced time-to-market by 35% compared to previous native development timeline
- Maintained performance benchmarks comparable to native applications
- Simplified compliance updates across both platforms simultaneously
Enterprise Field Service Application with Xamarin
A European utilities company developed a comprehensive field service application for their technicians using Xamarin:
- Leveraged existing .NET backend expertise and shared business logic
- Deployed across company-issued iOS tablets and Android phones
- Implemented complex offline capabilities with synchronized data
- Integrated with specialized equipment using custom native modules
- Reduced development costs by 45% compared to maintaining separate native apps
Choosing the Right Cross-Platform Approach
Selecting the optimal cross-platform framework requires evaluating multiple factors specific to your organization, project, and goals:
Decision Framework
Consider these key factors when making your decision:
Team Expertise
Evaluate your team's existing skills. React Native is ideal for teams with JavaScript/React experience, Flutter requires learning Dart, and Xamarin leverages C#/.NET knowledge.
Project Requirements
Analyze your application's technical needs, including UI complexity, performance requirements, hardware integrations, and platform-specific feature requirements.
Timeline and Budget
Consider development speed, learning curve, and resource availability. Some frameworks offer faster initial development but may require more platform-specific customization.
Long-term Maintenance
Evaluate framework maturity, corporate backing, community support, and ecosystem health to ensure long-term viability for your application.
Framework Selection Flowchart
This decision flowchart can help guide your framework selection process based on your specific priorities and constraints:
Implementation Roadmap
Once you've selected a framework, follow this implementation roadmap for cross-platform success:
- Proof of Concept: Develop a small prototype focusing on critical functionality and platform integrations
- Architecture Planning: Design a modular architecture that separates business logic, UI, and platform-specific code
- Development Environment Setup: Configure proper tooling, CI/CD pipelines, and testing infrastructure
- Incremental Development: Implement features in priority order, testing across platforms continuously
- Platform-Specific Customization: Address any platform-specific requirements or optimizations
- Quality Assurance: Conduct thorough testing across multiple device types and configurations
- Performance Optimization: Profile and optimize application performance on target devices
- Deployment Preparation: Prepare app store assets, review guidelines compliance, and plan phased rollout
Hybrid Approaches
In some cases, a hybrid approach combining cross-platform and native development may be optimal:
- Core + Native Modules: Develop the main application using a cross-platform framework but implement performance-critical or platform-specific features as native modules
- Feature-Based Separation: Develop certain features or screens natively while maintaining others cross-platform
- Progressive Migration: Gradually transition from a native codebase to cross-platform by implementing new features in the cross-platform framework
Michael Chen
Mobile Development Lead at Aries Star Marketing OPC
Michael has over 10 years of experience in mobile application development across native and cross-platform frameworks. He has led mobile development projects for clients in retail, finance, and healthcare sectors across Asia and the Middle East.
Ready to Build Your Cross-Platform Mobile Application?
Our expert team can help you select the right framework, design an optimal architecture, and develop a high-performance cross-platform application tailored to your business needs.
Schedule a Free Consultation